Document Type : Original Research Article
Authors
1 Neka Power Generation Management Company, Mazandaran, Iran
2 Department of Engineering, Sari Branch, Islamic Azad University, Sari, Iran
Abstract
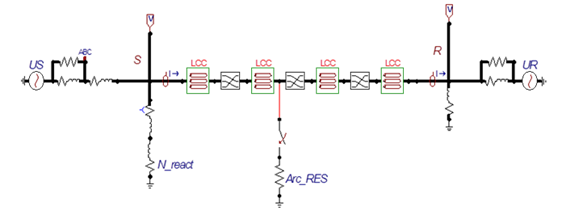
One of the most commonly used equipment in the power system, which is exposed to various types of faults for various reasons, is high and low voltage pressure cables. Due to the fact that cables, either power or distribution cables are mostly transported from underground, despite their further reliability in airway, they are more difficult to repair and possibly replace in case of fault, in line with this the correct fault detection and location of them is of utmost important. In this paper, as is clear from the title of the research, the Fourier transform and Modal transform methods are used to find the type and location of faults, so that the efficiency of the selected method for detecting and locating the faults in underground transmission cables is examined and the speed and accuracy of finding a solution to the problem is assessed. In this paper, it is expected that the Fourier transform method, followed by the Modal transform has substantial speed and accuracy in determining the type and location of the faults. Meanwhile, the detection and location indicators are used to determine the type and location of the fault, which as shown in the simulations, will have efficient performance. The sample model is simulated to demonstrate the correctness of these methods. The simulation results from MATLAB and EMTP/ATP software confirm the precise and rapid performance of the proposed method.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
- Fault detection and localization indicators
- Power cables
- Short circuit fault
- Fourier transform
- Clarke transform
- Modal components
Main Subjects
OPEN ACCESS
©2024 The author(s). This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
PUBLISHER NOTE
Sami Publishing Company remains neutral concerning jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
CURRENT PUBLISHER
Sami Publishing Company